微服务 的概念最早产生于Martin Fowler在2014年的一篇论文中。
微服务架构是一种架构模式,他提倡将单一应用程序划分成一组小的服务,服务与服务之间互相协调、相互配合,为用户提供最终价值。每个服务运行在独立的进程中,服务与服务之间采用轻量级的通信机制相互合作(通常是基于HTTP协议的Restful API)。每个服务围绕具体业务进行构建,并且能够被独立的部署到生产环境、类生产环境等。另外,应当尽量避免同一的、集中式的服务管理机制,对具有的一个服务而言,应当根据业务上下文,选择合适的语言、工具对其进行构建。
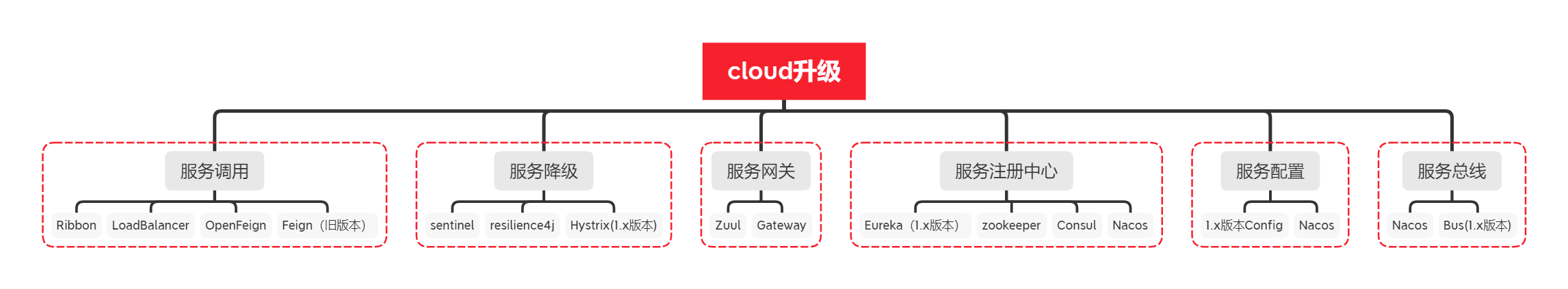
Cloud组件停更 被动修复bug,停更不停用,不再github上接收新的合并请求,不再发布新的版本。
RestTemplate提供了多种边界访问远程HTTP服务的方法,是一种简单便捷的访问restful服务模板类,是Spring提供的用于访问Rest服务的客户端模板工具集。
(URL,requestMap,ResponseBean.class)这三个参数分别代表REST请求地址,请求参数,HTTP响应转换的对象类型。
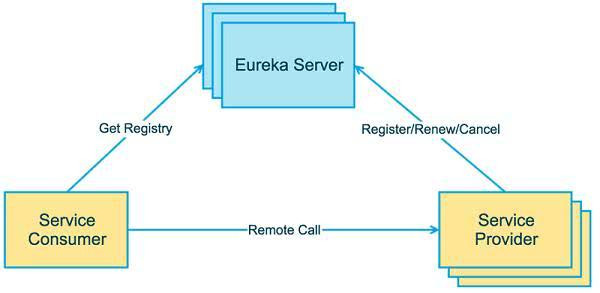
服务注册中心 Eureka服务注册中心 什么是服务治理 SpringCloud封装了Netflix公司开发的Eureka模块来实现服务治理。
在传统的RPC远程调用框架中,管理每个服务于服务之间依赖关系比较复杂,管理比较复杂,所以需要使用服务治理来管理服务与服务之间的依赖关系,可以实现服务调用、负载均衡、容错等,实现服务发现与注册。
服务注册与发现 Eureka采用来CS的设计架构,Eureka Server作为服务注册功能的服务器,他是服务注册中心。而系统中的其他微服务,使用Eureka客户端连接到Eureka Server并维持心跳链接。这样系统的维护人员可以通过Eureka Server来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行。
在服务注册与发现中,有一个注册中心,当服务器启动的时候,会把当前自己服务器的信息,比如服务地址,通讯地址等以别名的方式注册到注册中心中,另一方(其实也就是消费者或者服务提供者),以别名的方式去注册中心上获取实际的服务通信地址,然后在实现本地RPC调用。
RPC远程调用框架的思想在于:使用注册中心管理服务与服务之间的依赖关系。在任何RPC远程框架中都会有一个注册中心。
Eureka Server和Eureka Client Eureka Server提供服务注册
各个微服务节点通过配置启动后,会在Eureka Server中进行注册,这样Eureka Server中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用的节点信息,服务节点信息可以在界面中直观看到。
Eureka Client通过注册中心进行访问
这个客户端是用来简化Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时具备一个内置的,使用轮询负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认是30s一次),如果Serve在多个心跳周期内(默认90s)没有接收到某个节点的心跳,那就会被Server除名(从服务注册表中将节点移除)。
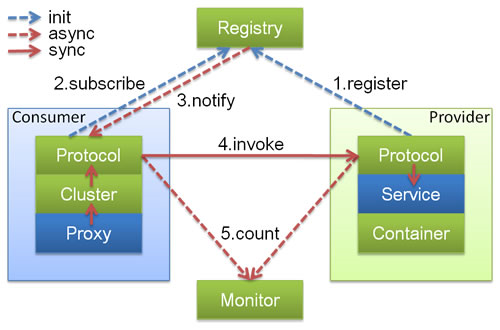
Eureka架构图与Dubbo对比
Eureka Server模块
1、创建模块
2、导入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <project xmlns ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" > <parent > <artifactId > cloud2020</artifactId > <groupId > org.xzq.springcloud</groupId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > </parent > <modelVersion > 4.0.0</modelVersion > <artifactId > cloud-eureka-server7001</artifactId > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.xzq.springcloud</groupId > <artifactId > cloud-api-commons</artifactId > <version > ${project.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > </dependency > </dependencies > </project >
3、编写配置文件
application.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 server: port: 7001 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false service-url: defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
4、创建主类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer public class EurekaMain7001 { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaMain7001.class,args); } }
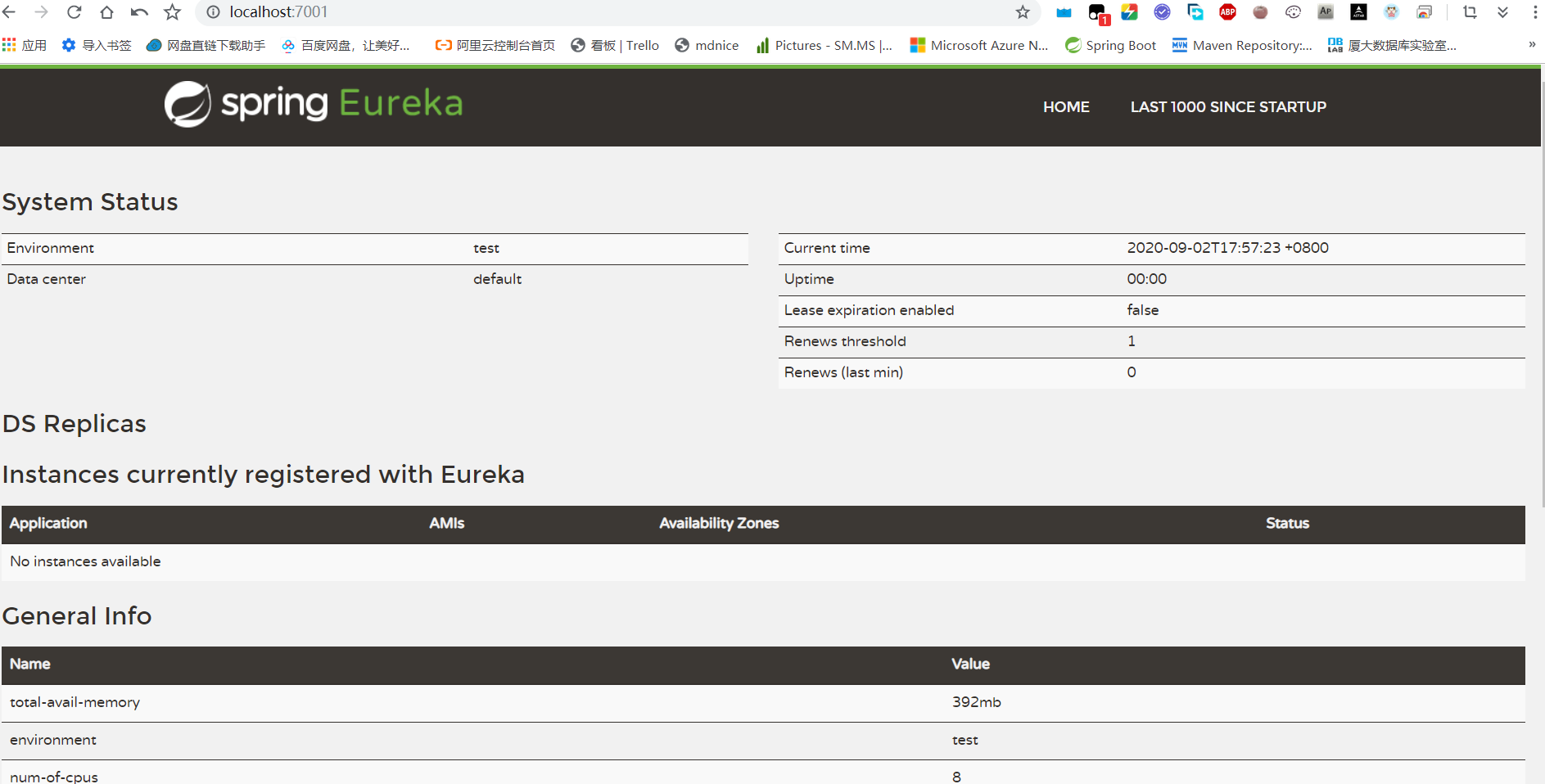
5、启动server,访问http://localhost:7001
Eureka集群原理 先启动Eureka注册中心,启动服务提供者,支付服务启动后会把自身信息以别名的方式注册进Eureka,消费者order服务在需要调用接口时,使用服务别名去注册中心获取实际的远程调用地址,消费者获取调用地址后,底层使用的是HTPPClient技术实现远程调用,消费者获得服务地址后会魂村到本地JVM内存中,默认每隔30s更新一次服务调用地址。
要实现RPC远程调用服务最核心的是高可用,但是如何实现高可用?
方法:搭建注册中心集群,实现负载均衡+故障容错。
服务注册中心搭建集群,集群中的所有服务都相互注册,例如server7001,server7002,7002的eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,而7001中的Eureka配置是eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka。在主启动类上添加`@EnableEurekaServer`注解,先启动这些注册中心服务,再启动服务提供者,最后启动消费者。
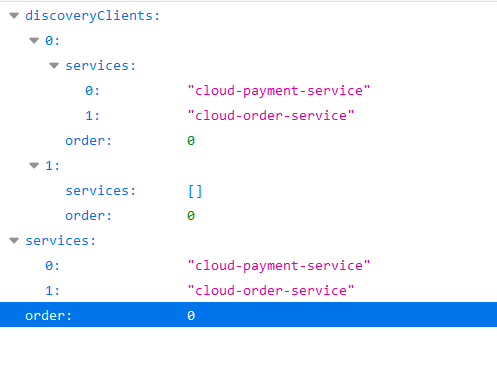
服务发现Discovery 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @RequestMapping("/payment") @RestController @Slf4j public class PaymentController { @Autowired private PaymentService paymentService; @Value("${server.port}") private String serverPort; @Resource private DiscoveryClient discoClient; @GetMapping("/discover") public Object discovery () { List<String> services = discoClient.getServices(); for (String service : services) { log.info("service====" +service); } List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE" ); for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) { log.info(instance.getInstanceId()+"\t" +instance.getHost()+"\t" +instance.getPort()+"\t" +instance.getUri()); } return this .discoClient; } }
在主启动类上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @EnableDiscoveryClient public class Payment8002 { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Payment8002.class,args); } }
通过浏览器访问localhost:8001/payment/discover
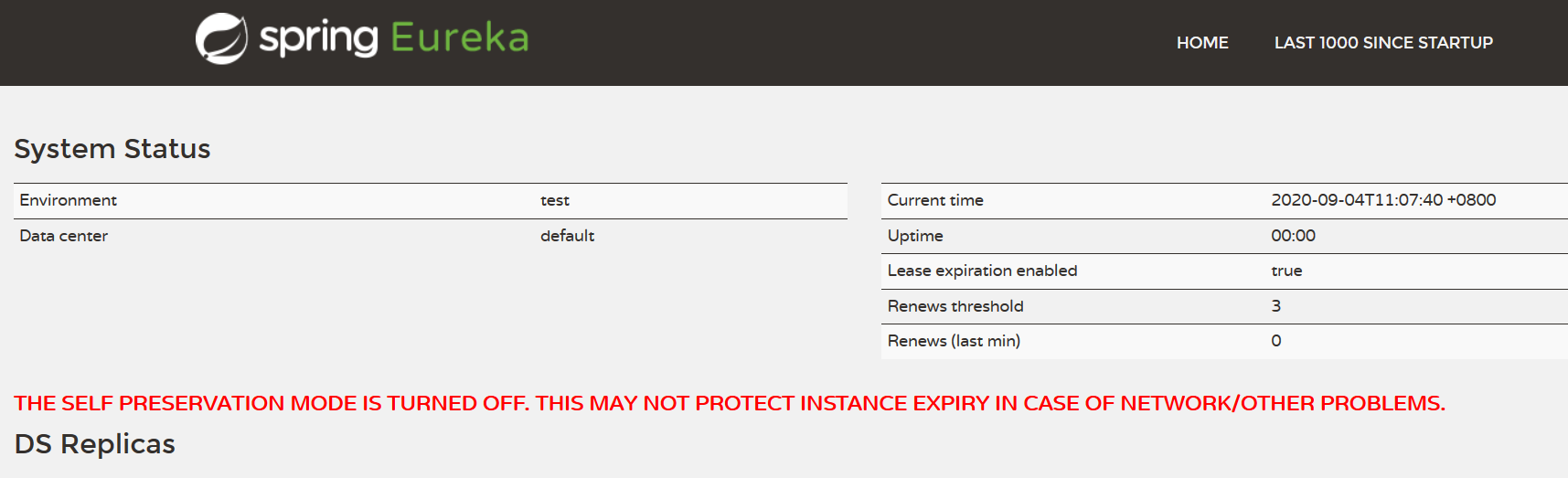
Eureka的自我保护 所谓的保护模式就是用于一组客户端和Eureka Server之间存在网络分区场景下的保护。一旦进入保护模式,Eureka Server将会尝试保护其服务注册表中的信息,不再删除服务注册表中的数据,也就是不会注销任何微服务。
如果在Eureka Server的首页看到以下这段提示,则说明Eureka进入了保护模式:
EMERGENCY! EUREKA MAY BE INCORRECTLY CLAIMING INSTANCES ARE UP WHEN THEY’RE NOT. RENEWALS ARE LESSER THAN THRESHOLD AND HENCE THE INSTANCES ARE NOT BEING EXPIRED JUST TO BE SAFE.
一句话:在某时刻一个微服务不可用,Eureka不会立刻清理,依旧会对改为服务的信息进行保护。
这是属于CAP里面的AP分支。
怎样禁止自我保护? 在Eureka-server中,修改配置文件,添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 server: port: 7001 eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7001.com client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/ server: port: 7001 eureka: instance: hostname: eureka7001.com client: register-with-eureka: false fetch-registry: false service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/ server: enable-self-preservation: false eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000
enable-self-preservation: false # 关闭自我检测,一旦关闭自我检测,其中有任何一台微服务宕机,Eureka就会立刻将他从注册中心除名。
将其中的一个服务提供者的配置也更改如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 eureka: client: register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka instance: instance-id: payment8001 prefer-ip-address: true lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2 lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1
1 2 eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds=2 eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds=1
客户端默认间隔是30s,向服务端发送心跳,改成每隔1s向服务端发送心跳。
启动服务后,访问http://eureka7001.com:7001/
当关闭payment8001服务提供者后,实例立即消失。
使用zookeeper作服务发现与注册时,服务节点是临时节点。当服务关闭时,zookeeper会立即去除实例。
导入zookeeper相关的依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.xzq.springcloud</groupId > <artifactId > cloud-api-commons</artifactId > <version > ${project.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery</artifactId > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.apache.zookeeper</groupId > <artifactId > zookeeper</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.zookeeper</groupId > <artifactId > zookeeper</artifactId > <version > 3.4.13</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies > server: port: 8004 spring: application: name: cloud-provider-payment #微服务实例名 cloud: zookeeper: connect-string: localhost:2181 #zookeeper服务所在的IP地址,默认端口是2181
之后启动zookeeper服务,并打开zkCli.sh,ls /services,会发现实例名成是cloud-provider-payment。
Consul简介 官网地址:https://www.consul.io/docs
Consul是一套开源的分布式服务发现和配置管理系统,有HashiCorp公司使用Go语言开发。
提供了微服务系统中的服务治理、配置中心、控制总线 等功能。
这些功能中的每一个否可以根据自己的需要单独使用,也可以一起使用构成全方面的服务网格,总之Consul提供了一种完整的服务网格解决方案。
它具有很多优点。包括:基于raft协议,比较简洁;支持健康检查,同时支持HTTP和DNS协议支持扩数据中心的WAN集群,提供图形界面 扩平台支持,例如Linux,Mac,Windows。
Consul安装与配置 Consul下载地址: https://www.consul.io/downloads
选择你所对应的版本,下载压缩包后,直接解压。
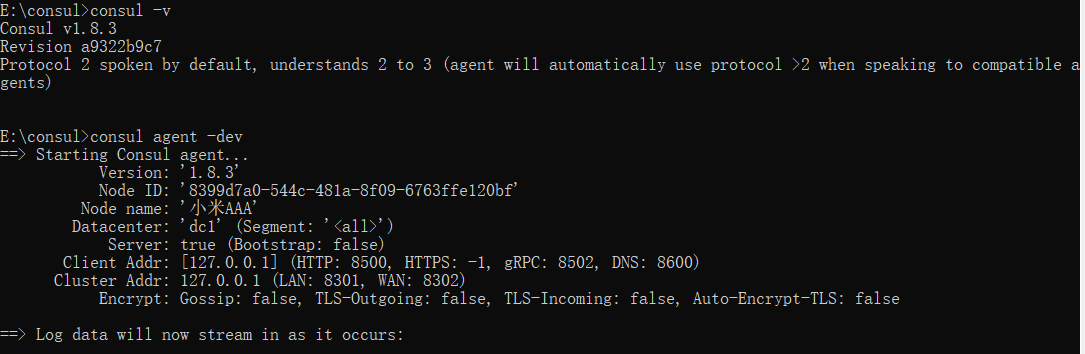
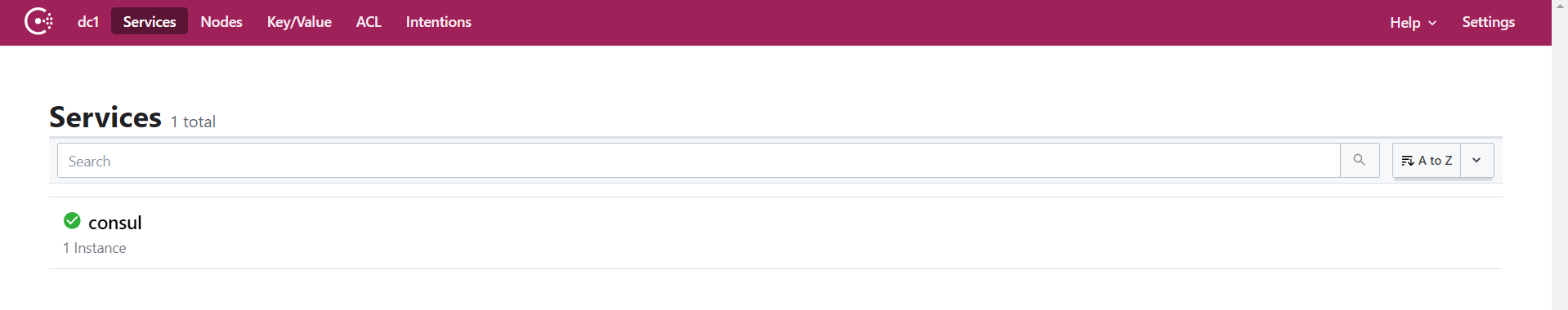
解压完成后,只有一个consul.exe文件,通过cmd窗口,输入consul agent -dev 启动,然后通过浏览器访问localhost:8500,得到以下界面,算是安装完成了。
CAP原则 最多只能同时满足两个。
CAP理论的核心就是:一个分布式系统不可能同时很好的满足一致性,可用性和分区容错性,这三个需求。
因此,根据CAP原理将NoSQL数据库分成了满足CA原则,满足CP原则和满足AP原则三大类。
CA-单点集群,满足一致性,可用性的系统,通常在可扩展性上不强大。
CP-满足一致性,分区容错性,通常性能上有所损失。(Zookeeper/Consul)
AP-满足可用性,分区容错性的系统,通常可能对一致性的要其余不是很严格。(Eureka)
组件名
语言
CAP
服务健康检测
对外暴露接口
SpringCloud集成
Eureka
Java
AP
可配支持
HTTP
已集成
Consul
Go
CP
支持
HTTP/DNS
已集成
Zookeeper
Java
CP
支持
客户端
已集成
Ribbon简单概述 SpringCloud Ribbon是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端。(负载均衡工具)
简单的说,Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法和服务调用 。Ribbon客户端主键提供一系列完善的配置项:如连接超时,重试等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Blance后面的所有机器,Ribbon会自动帮助你基于某种规则去连接这些机器。我们很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
虽然现在Ribbon已经停止维护,但是还是有不少人使用。
主要的模块有Ribbon-HTTPClient,Ribbon-eureka,Ribbon-Loadbalance
所谓的负载均衡是什么? 简单的说就是将用户的请求分发到多个服务上,从而达到系统的高可用。
常见的负载均衡有Nginx,LVS,硬件F5等。
Ribbon本地负载均衡VS Nginx服务端负载均衡Nginx是服务器负载均衡,客户端所有请求都会交给Nginx,然后由Nginx实现转发请求。即负载均衡是服务端实现的。
Ribbon是本地负载均衡,在调用微服务接口的时候,会在注册中心上获取注册信息,缓存到JVM本地,从而在本地实现RPC远程调用服务技术。
Ribbon负载均衡是客户端本地的负载均衡,分为集中式和进程内。
集中式
在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的负载均衡设施(可以是硬件,如F5,也可以是软件,如Nginx),由该设施负责访问请求,通过某种策略转发到服务的提供方。
进程式
将负载均衡的逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。Ribbon属于进程内的负载均衡。他是一个类库,继承消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
Ribbon是一个软负载均衡的客户端组件,它可以和其他所需请求的客户端结合使用,例如Eureka,RestTemplate等。
Ribbon的工作原理:第一步先选择EurekaServer,他会优先选择在同一个区域内负载均衡较少的Server。
第二步再根据用户指定的策略,从Server取到的服务注册列表中选择一个地址。
其中Ribbon提供了多种策略:比如轮询,随机,根据响应时间加权等。
Ribbon依赖如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId > <version > 2.2.1.RELEASE</version > <scope > compile</scope > </dependency >
默认情况下,Eureka-client依赖中包含有ribbon的依赖,不需要再次引入。
RestTemplate中的getForEntity方法返回的是对象,getForObject方法返回的是JSON串。
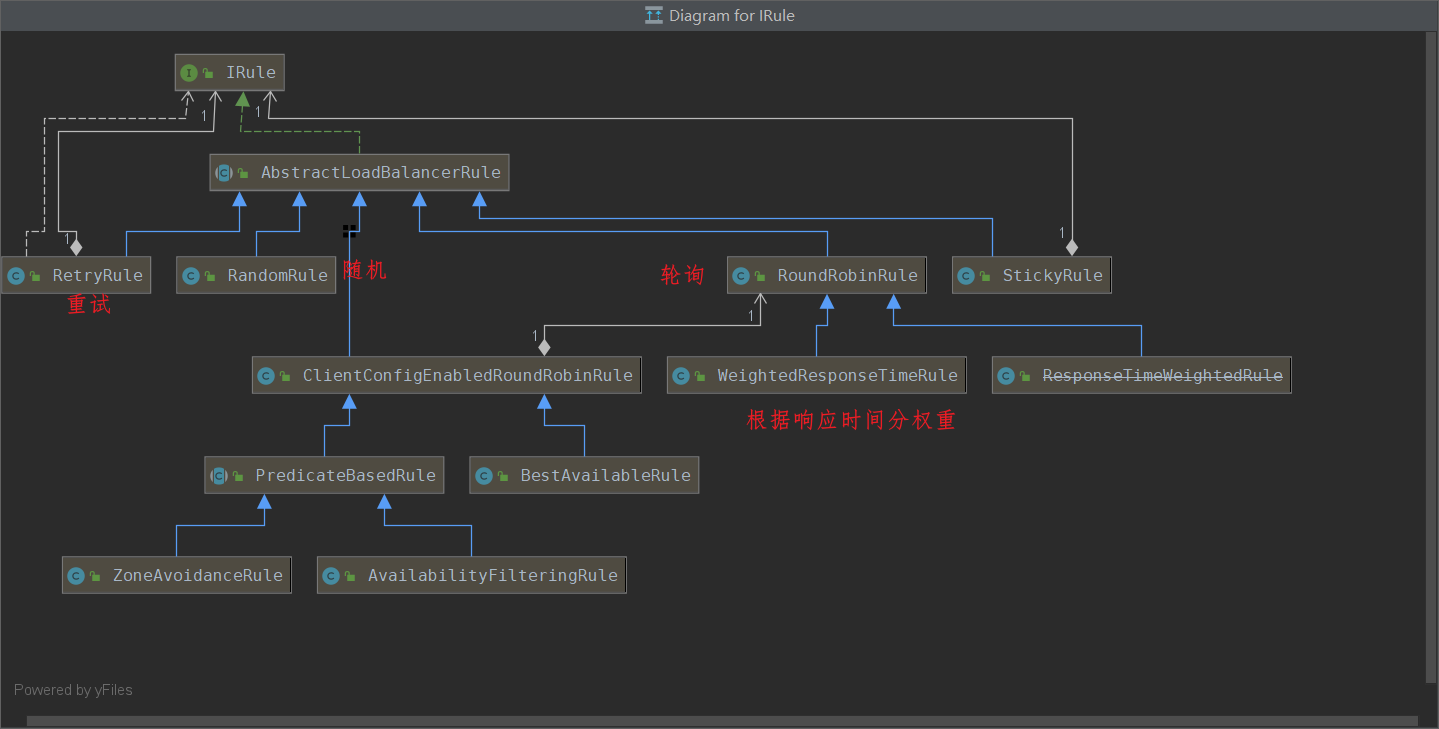
Ribbon的核心组件IRule Ribbon默认的负载均衡算法是轮询,而IRule是根据特定的算法中从服务列表中选取其中一个要访问的服务。
一共有7个方法。
修改负载均衡算法 将默认的轮询改为随机。
首先增加配置类,需要注意的是,自定义的配置类不能被@ComponentScan注解扫描到,所以自定义的IRule不要放在启动类的子目录,要与启动类隔离开。
MySelfRule类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration public class MySelfRule { @Bean public IRule getRule () { return new RandomRule (); } }
第二步,需要在主启动类上添加@RibbonClient注解。然后再启动。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = MySelfRule.class) public class OrderMain80 { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args ); } }
启动Eureka-server,启动服务提供者payment8001,payment8002,启动服务消费者consumer-order80.
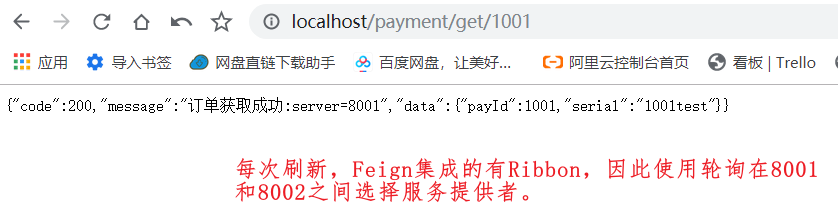
访问http://localhost/consumer/payment/getForEntity/1001,会发现被访问的服务提供者的端口是随机变化的,因此选取的服务也是随机的。
Ribbon负载均衡算法原理 轮询方法:rest接口第几次请求数对服务集群总数量取余操作,得到结果就是实际调用服务器的下标,每次服务器重启后rest接口计数从1开始。
例如有两台服务提供者,instances[0] = 127.0.0.1:8001,instances[1] = 127.0.0.1:8002,两台实例作为两台机器,集群总数是2,按照轮询算法原理。
当第1请求时, 1%2 = 1,所以获取服务地址是127.0.0.1:8001;
当第2请求时, 2%2 = 0,所以获取服务地址是127.0.0.1:8002;
当第3请求时, 3%2 = 1,所以获取服务地址是127.0.0.1:8001;
当第4请求时, 4%2 = 0,所以获取服务地址是127.0.0.1:8002;
以此类推…
手写轮询负载均衡算法 首先创建一个MyLoadBalance接口
1 2 3 4 public interface MyLoadBalance { ServiceInstance instances (List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances) ; }
接口的实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Component @Slf4j public class MyLoadBalanceImpl implements MyLoadBalance { private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger (0 ); public final int getAndIncrement () { int current = 0 ; int next; do { current = this .atomicInteger.get(); next = current > 2147483647 ? 0 : current+1 ; }while (!this .atomicInteger.compareAndSet(current,next)); log.info("next= " +next); return next; } @Override public ServiceInstance instances (List<ServiceInstance> serviceInstances) { int index = getAndIncrement() % serviceInstances.size(); return serviceInstances.get(index); } }
服务消费者使用这种轮询方法,选取服务提供者。orderController
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/lb") public String getPaymentUrl () { String serviceID = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE" ; List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceID); if (instances == null || instances.size() <=0 ){ return null ; } ServiceInstance instances1 = loadBalance.instances(instances); URI uri = instances1.getUri(); log.info("url= " +uri); return restTemplate.getForObject(uri+"/payment/lb" ,String.class); }
OpenFeign的基本概念Feign是一个声明式WebService客户端。使用Feign能让编写WebService客户端更加简单。
他的使用方法是:定义一个服务接口然后在上面添加注解。Feign也能支持可拔插式的编码器和解码器。Spring Cloud对Feign进行了封装,使其能够支持SpringMVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters。Feign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用完成负载均衡。
Feign旨在使Java Http客户端变得更加容易。
前面在使用Ribbon+RestTemplate时,利用RestTemplate对Http请求做封装处理,形成一套模板话的调用方法。但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用。所以,Feign在此基础上做了进一步的封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现接口。在Feign的实现下,我们只需要使用注解配置接口,即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring Cloud Ribbon时,自己封装服务调用的工作量。
还有一点,默认Feign也已经集成了Ribbon。
OpenFeign的使用 1、新建cloud-consumer-fegin-order80模块,
2、修改pom.xml
添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.xzq.springcloud</groupId > <artifactId > cloud-api-commons</artifactId > <version > ${project.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > <optional > true</optional > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies >
3、创建application.yml配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 server: port: 80 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka register-with-eureka: false
4、写主启动类
注意是@Feign注解生效,需要在主启动类上添加@EnableFeignClients。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @SpringBootApplication @EnableFeignClients public class OpenFeignMain80 { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OpenFeignMain80.class,args); } }
5、编写业务类
service
1 2 3 4 5 6 @FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE") @Component public interface PaymentFeignService { @GetMapping("/payment/get/{id}") CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById (@PathVariable("id") Long id) ; }
controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RestController @Slf4j public class OrderFeignController { @Resource private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService; @GetMapping("/payment/get/{id}") public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById (@PathVariable("id") Long id) { return paymentFeignService.getPaymentById(id); } }
6、测试feign功能
启动两个Eureka-server,启动payment-8001,payment-8002,然后再启动feign-order80.
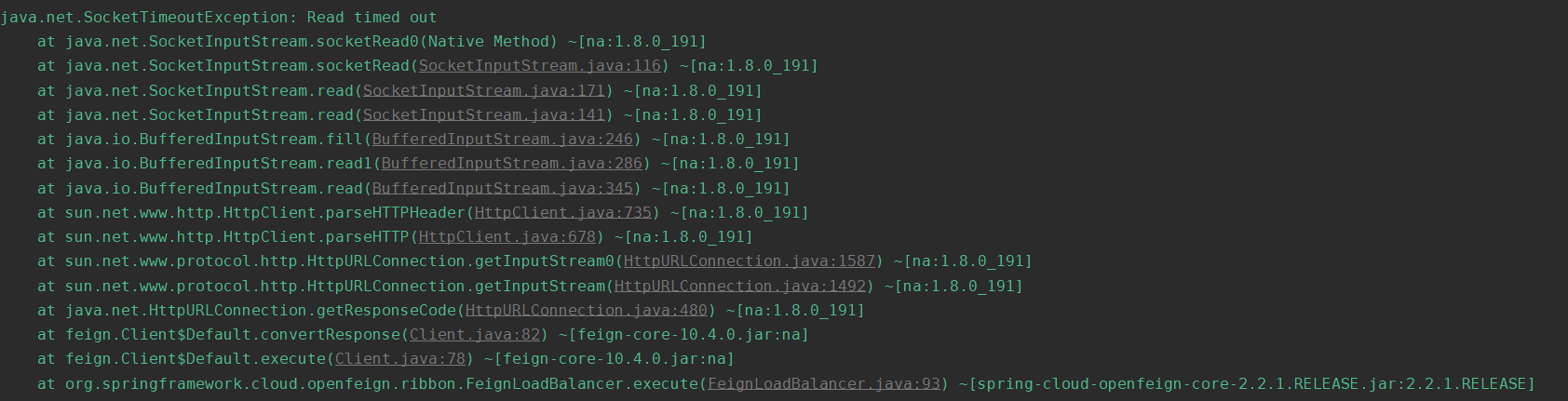
OpenFeign的超时控制 问题描述:在消费者向服务提供者发起请求到最后完成响应的过程中,如果服务提供者在处理过程中消耗的时间大于客户端消费者等待的时间,客户端就会java.net.SocketTimeoutException: Read timed out抛出异常。
解决方法:在配置文件中,修改客户端读取时间和连接时间尽量让消费者等待的时间大于提供者处理的时间。这个也就是Feign的超时控制。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 server: port: 80 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka,http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka register-with-eureka: false ribbon: ReadTimeout: 5000 ConnectTimeout: 5000
OpenFeign的日志增强 支持的日志级别
NONE:默认的,不显示任何日志
BASIC:仅仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码以及执行时间
HEADERS:除了BASIC中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的头信息
FULL:除了HEADERS中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的正文以及元数据。
要想在控制台中查看详细日志,需要设置配置类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Configuration public class FeginLogConfig { @Bean Logger.Level feignLogger () { return feign.Logger.Level.FULL; } }
配置文件中添加需要打印日志的请求方法路径。
1 2 3 logging: level: com.guigu.service.PaymentFeignService: debug
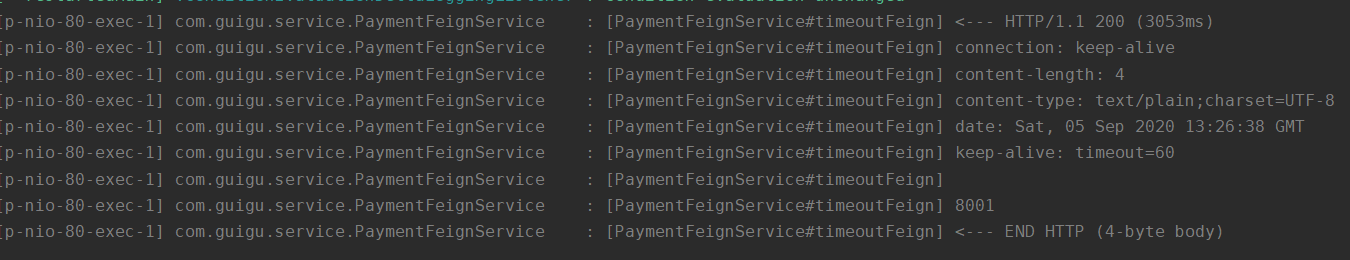
启动服务后,向服务提供方发起请求,在控制台上可以看到以下日志。
未完待续…下一篇:Hystrix
参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18E411x7eT